tsignal-python
TSignal
TSignal is a lightweight, pure-Python signal/slot library that provides thread-safe, asyncio-compatible event handling inspired by the Qt signal/slot pattern—but without the heavyweight Qt dependencies. It enables clean decoupling of components, seamless thread-to-thread communication, and flexible asynchronous/synchronous slot handling.
Key Features
- Pure Python: No Qt or external GUI frameworks needed.
- Async/Await Friendly: Slots can be synchronous or asynchronous, and integrate seamlessly with asyncio.
- Thread-Safe: Signal emissions and slot executions are automatically managed for thread safety.
- Flexible Connection Types: Direct or queued connections, automatically chosen based on the caller and callee threads.
- Worker Thread Pattern: Simplify background task execution with a built-in worker pattern that provides an event loop and task queue in a dedicated thread.
- Familiar Decorators: Inspired by Qt’s pattern,
@t_with_signals,@t_signal, and@t_slotlet you define signals and slots declaratively. - Weak Reference:
- By setting
weak=Truewhen connecting a slot, the library holds a weak reference to the receiver object. This allows the receiver to be garbage-collected if there are no other strong references to it. Once garbage-collected, the connection is automatically removed, preventing stale references.
- By setting
Why TSignal?
Modern Python applications often rely on asynchronous operations and multi-threading. Traditional event frameworks either require large external dependencies or lack seamless async/thread support. TSignal provides:
- A minimal, dependency-free solution for event-driven architectures.
- Smooth integration with asyncio for modern async Python code.
- Automatic thread-affinity handling so cross-thread signals “just work.”
- Decorator-based API that’s intuitive and maintainable.
Key Benefits
Async-Ready
- Built for modern asyncio workflows
- Define async slots that are invoked without blocking your event loop
Thread-Safe by Design
- Signals are dispatched to the correct thread or event loop
- No manual lock management required
Flexible Slots
- Connect to class methods, standalone functions, or lambdas
- Support for both strong and weak references
Robust Testing & Examples
- Comprehensive test coverage
- Real-world examples including GUI applications
- Best practices demonstrated throughout
Installation
TSignal requires Python 3.10 or higher.
git clone https://github.com/TSignalDev/tsignal-python.git
cd tsignal-python
pip install -e .
For development (includes tests and linting tools):
pip install -e ".[dev]
Quick Start
Basic Example
from tsignal import t_with_signals, t_signal, t_slot
@t_with_signals
class Counter:
def __init__(self):
self.count = 0
@t_signal
def count_changed(self):
pass
def increment(self):
self.count += 1
self.count_changed.emit(self.count)
@t_with_signals
class Display:
@t_slot
async def on_count_changed(self, value):
print(f"Count is now: {value}")
# Connect and use
counter = Counter()
display = Display()
counter.count_changed.connect(display, display.on_count_changed)
counter.increment() # Will print: "Count is now: 1"
Asynchronous Slot Example
@t_with_signals
class AsyncDisplay:
@t_slot
async def on_count_changed(self, value):
await asyncio.sleep(1) # Simulate async operation
print(f"Count updated to: {value}")
# Usage in async context
async def main():
counter = Counter()
display = AsyncDisplay()
counter.count_changed.connect(display, display.on_count_changed)
counter.increment()
# Wait for async processing
await asyncio.sleep(1.1)
asyncio.run(main())
Core Concepts
Signals and Slots
- Signals: Declared with
@t_signal. Signals are attributes of a class that can be emitted to notify interested parties. - Slots: Declared with
@t_slot. Slots are methods that respond to signals. Slots can be synchronous or async functions. - Connections: Use
signal.connect(receiver, slot)to link signals to slots. Connections can also be made directly to functions or lambdas.
Thread Safety and Connection Types
TSignal automatically detects whether the signal emission and slot execution occur in the same thread or different threads:
- Auto Connection: When connection_type is AUTO_CONNECTION (default), TSignal checks whether the slot is a coroutine function or whether the caller and callee share the same thread affinity. If they are the same thread and slot is synchronous, it uses direct connection. Otherwise, it uses queued connection.
- Direct Connection: If signal and slot share the same thread affinity, the slot is invoked directly.
- Queued Connection: If they differ, the call is queued to the slot’s thread/event loop, ensuring thread safety.
This mechanism frees you from manually dispatching calls across threads.
Worker Threads
For background work, TSignal provides a @t_with_worker decorator that:
- Spawns a dedicated event loop in a worker thread.
- Allows you to queue async tasks to this worker.
- Enables easy start/stop lifecycle management.
- Integrates with signals and slots for thread-safe updates to the main
Worker Example
from tsignal import t_with_worker, t_signal
@t_with_worker
class DataProcessor:
@t_signal
def processing_done(self):
"""Emitted when processing completes"""
async def run(self, *args, **kwargs):
# The main entry point for the worker thread’s event loop
# Wait for tasks or stopping signal
await self._tsignal_stopping.wait()
async def process_data(self, data):
# Perform heavy computation in the worker thread
result = await heavy_computation(data)
self.processing_done.emit(result)
processor = DataProcessor()
processor.start()
# Queue a task to run in the worker thread:
processor.queue_task(processor.process_data(some_data))
# Stop the worker gracefully
processor.stop()
From Basics to Practical Use Cases
We’ve expanded TSignal’s examples to guide you from simple demos to full-fledged applications. Each example has its own GitHub link with fully commented code.
For detailed explanations, code walkthroughs, and architecture diagrams of these examples, check out our Examples Documentation.
Basic Signal/Slot Examples
- signal_basic.py and signal_async.py
- demonstrate how to define simple synchronous and async slots.
- signal_function_slots.py and signal_lambda_slots.py
- show how you can connect signals to standalone functions and lambdas.
Multi-Threading and Workers
- thread_basic.py and thread_worker.py
- walk you through multi-threaded setups, including background tasks and worker loops.
- You’ll see how signals emitted from a background thread are properly handled in the main event loop or another thread’s loop.
Stock Monitor (Console & GUI)
- stock_monitor_simple.py
- A minimal stock monitor that periodically updates a display. Perfect for learning how TSignal can orchestrate real-time updates without blocking.
- stock_monitor_console.py
- A CLI-based interface that lets you type commands to set alerts, list them, and watch stock data update in real time.
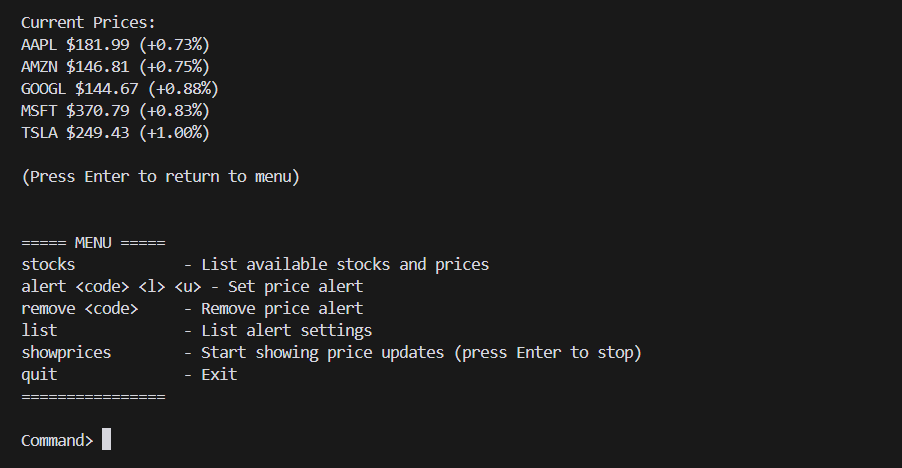
Stock Monitor Console: Real-time price updates, alert configuration, and notification history in action
- stock_monitor_ui.py
- A more elaborate Kivy-based UI example showcasing real-time stock monitoring. You’ll see how TSignal updates the interface instantly without freezing the GUI. This example underscores how TSignal’s thread and event-loop management keeps your UI responsive and your background tasks humming.
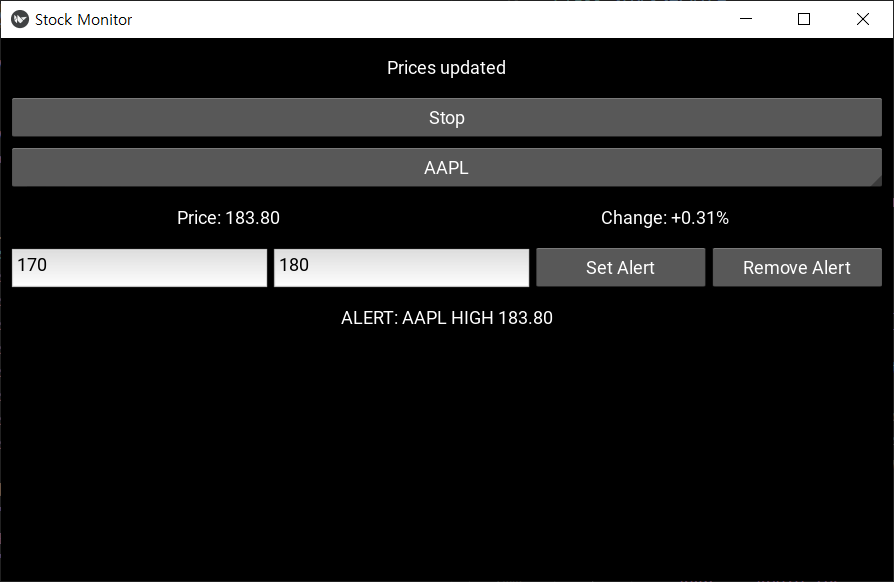
Stock Monitor UI: Real-time price updates, alert configuration, and notification history in action
Together, these examples highlight TSignal’s versatility—covering everything from quick demos to production-like patterns with threads, queues, and reactive UI updates.
Documentation and Example
- Usage Guide: Learn how to define signals/slots, manage threads, and structure your event-driven code.
- API Reference: Detailed documentation of classes, decorators, and functions.
- Examples: Practical use cases, including UI integration, async operations, and worker pattern usage.
- Logging Guidelines: Configure logging levels and handlers for debugging.
- Testing Guide: earn how to run tests and contribute safely.
Get Started
- Visit the GitHub Repository
- Find installation instructions, usage docs, and a variety of real-world examples.
- Try the Python Release
- Run pip install tsignal (requires Python 3.10+).
- Check out the docs and examples in the repository’s examples/ folder.
- Contribute / Give Feedback
- We appreciate your thoughts on the current Python version.
- We welcome contributions! Please read our Contributing Guidelines before submitting PRs.
License
TSignal is licensed under the MIT License. See LICENSE for details.